Quantitative description of the effect of slag surface area on its reaction kinetics in sodium silicate-activated materials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21809/rilemtechlett.2022.167Keywords:
Surface Area, Alkali-Activated Materials, Reaction Kinetics, Slag, ReactivityAbstract
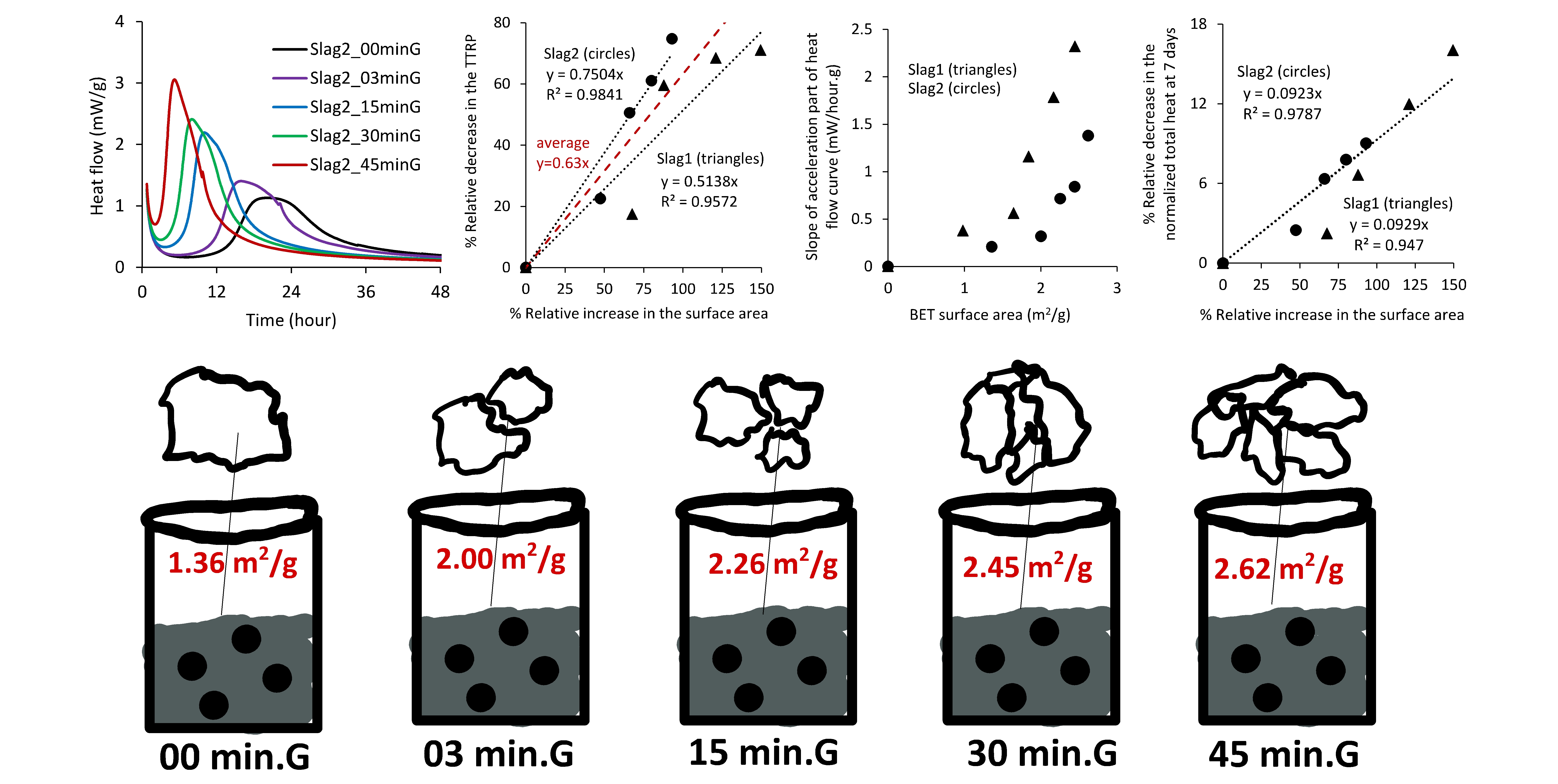
The effects of chemical oxides and the surface area (SA) of slags on the initial reactivity of alkali-activated materials (AAMs) are coupled. It is well known that the reactivity of slag in AAMs is impacted by the SA, however, a quantitative measure of this effect was not provided in previous studies. For a proper understanding of the effect of slag chemistry on the reaction kinetics of AAMs, a quantitative description of the slags SA's effect is required. The reaction kinetics in the activated slags were monitored using isothermal calorimetry. The SAs of the pulverised slags were linked to the time-to-reach-the-main-peak (TTRP) of the reaction, the slope of the acceleration part of the main peak, and the total heat at one, three, and seven days. A 100% relative increase in SA caused a ~51%-75% relative decrease in TTRP. The slope of the acceleration stage also considerably increased with the SA of the slags. However, the effect of the SAs on the total heat was only distinct up to three days and then considerably reduced at seven days. The result of this study indicates that the effect of SA on the initial reactivity of AAMs cannot be simply considered using the proportional contribution. The outcome of this study can provide a promising measure to decouple the effects of SAs and the chemical compositions of slags on the reaction kinetics of AAMs by providing quantitative results for the effect SAs.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Abdelrahman Hamdan, Taehwan Kim, Ailar Hajimohammadi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright of the articles published in RILEM Technical Letters and grant the journal the right of first publication with open access. The work is simultaneously licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) that allows others to share and adapt the work under the following terms: 1) a proper attribution is given in a form of bibliographic record with the DOI link directing to RILEM Technical Letters; 2) a link to the license is provided; 3) the changes (if any) are indicated.









