Applications of physics-informed neural networks for property characterization of complex materials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21809/rilemtechlett.2022.174Keywords:
Artificial neural networks, Construction material characterization, Physics-informed neural networks, Porous media flow, Wave propagationAbstract
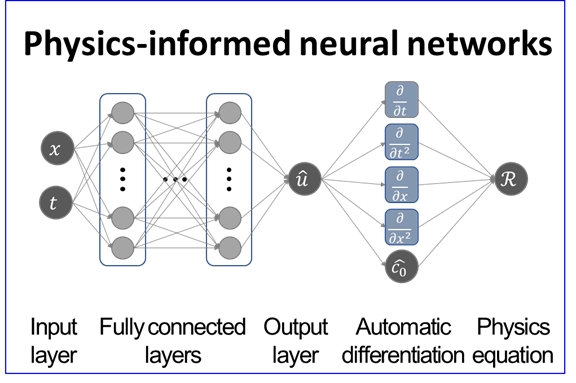
The characterization of in-place material properties is important for quality control and condition assessment of the built infrastructure. Although various methods have been developed to characterize structural materials in situ, many suffer limitations and cannot provide complete or desired characterization, especially for inhomogeneous and complex materials such as concrete and rock. Recent advances in machine learning and artificial neural networks (ANN) can help address these limitations. In particular, physics-informed neural networks (PINN) portend notable advantages over traditional physics-based or purely data-driven approaches. PINN is a particular form of ANN, where physics-based equations are embedded within an ANN structure in order to regularize the outputs during the training process. This paper reviews the fundamentals of PINN, notes its differences from traditional ANN, and reviews applications of PINN for selected material characterization tasks. A specific application example is presented where mechanical wave propagation data are used to characterize in-place material properties. Ultrasonic data are obtained from experiments on long rod-shaped mortar and glass samples; PINN is applied to these data to extract inhomogeneous wave velocity data, which can indicate mechanical material property variations with respect to length.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Sangmin Lee, John S. Popovics

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright of the articles published in RILEM Technical Letters and grant the journal the right of first publication with open access. The work is simultaneously licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) that allows others to share and adapt the work under the following terms: 1) a proper attribution is given in a form of bibliographic record with the DOI link directing to RILEM Technical Letters; 2) a link to the license is provided; 3) the changes (if any) are indicated.









