Thermal conductivity of porous building materials: An exploration of new challenges in fractal modelling solutions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21809/rilemtechlett.2023.178Keywords:
Fractal geometry, heat transfer, modelling, porous building materials, thermal conductivityAbstract
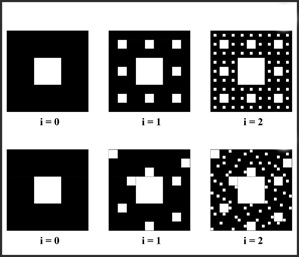
The improvement in the insulation material performance is one of the recent crucial problems. The energy consumption in the construction and buildings field has a significant impact on the society and the environment. For these reasons, researchers have focused on studying their thermal behaviour in order to improve fabrication methods and material design structures. In this sense, a great contribution has been offered by the modeling procedures. A remarkable attention has been dedicated to the application of fractal geometry which seems to be a promising method to replicate the porous structures as well as to predict the effective thermal conductivity. In this paper, a review of different modeling procedures is presented, comparing both traditional and fractal theory-based approaches. Fractal models demonstrate high reliability in reproducing experimental data under various conditions, including dry and moist systems. This is further enhanced by the application of recursive formulas, which streamline calculations even for complex porous microstructures. The choice between one model and another depends on the specific characteristics of the materials under study. In all cases, the versatility of the analytical procedures enables one to achieve a remarkable agreement with experimental data.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Giorgio Pia, Marta Cappai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright of the articles published in RILEM Technical Letters and grant the journal the right of first publication with open access. The work is simultaneously licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) that allows others to share and adapt the work under the following terms: 1) a proper attribution is given in a form of a reference to the original work's authorship and initial publication in RILEM Technical Letters (bibliographic record with the DOI link); 2) a link to the license is provided; 3) the changes (if any) are indicated.









