Biomineralization in cement and concrete research
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21809/rilemtechlett.2023.187Keywords:
Biomineralization, Cement, Concrete, Calcium Carbonate, Silicon DioxideAbstract
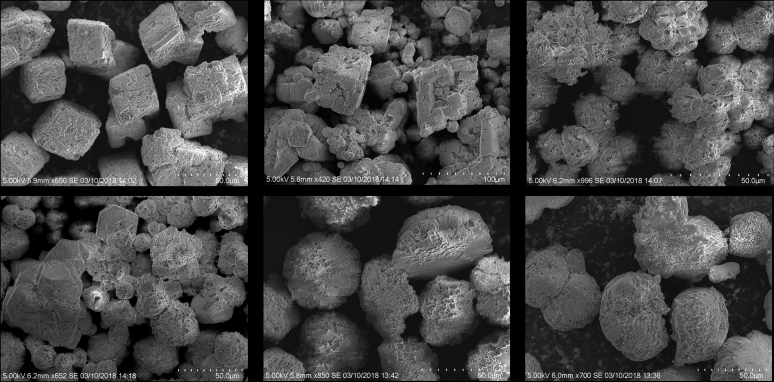
Biomineralization refers to the biological processes through which living organisms produce minerals. In recent years, biomineralizing microorganisms have been used to stabilize soil or to impart a self-healing or self-sealing mechanism to damaged cement and concrete materials. However, applications of biominerals in cement and concrete research can extend far beyond these applications. This article focuses on the biomineralization of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and silicon dioxide (SiO2) and their past, present, and future potential applications in cement and concrete research. First, we review the mechanisms of CaCO3 and SiO2 biomineralization and the micro- and macroorganisms involved in their production. Second, we showcase the wide array of biomineral architectures, with an explicit focus on CaCO3 polymorphs and SiO2 morphologies found in nature. Third, we briefly summarize previous applications of CaCO3 and SiO2 biomineralization in cement and concrete research. Finally, we discuss emerging applications of biominerals in cement and concrete research, including mineral admixtures or raw meal for portland cement production, as well as other applications that extend beyond self-healing.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Nicolas Dowdy, Wil Srubar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright of the articles published in RILEM Technical Letters and grant the journal the right of first publication with open access. The work is simultaneously licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) that allows others to share and adapt the work under the following terms: 1) a proper attribution is given in a form of bibliographic record with the DOI link directing to RILEM Technical Letters; 2) a link to the license is provided; 3) the changes (if any) are indicated.









