Utilization of volcanic ejecta as a high-performance supplementary cementitious material by gravity classification and pulverization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21809/rilemtechlett.2018.66Keywords:
volcanic glass, natural pozzolan, supplementary cementitious material, high performance concreteAbstract
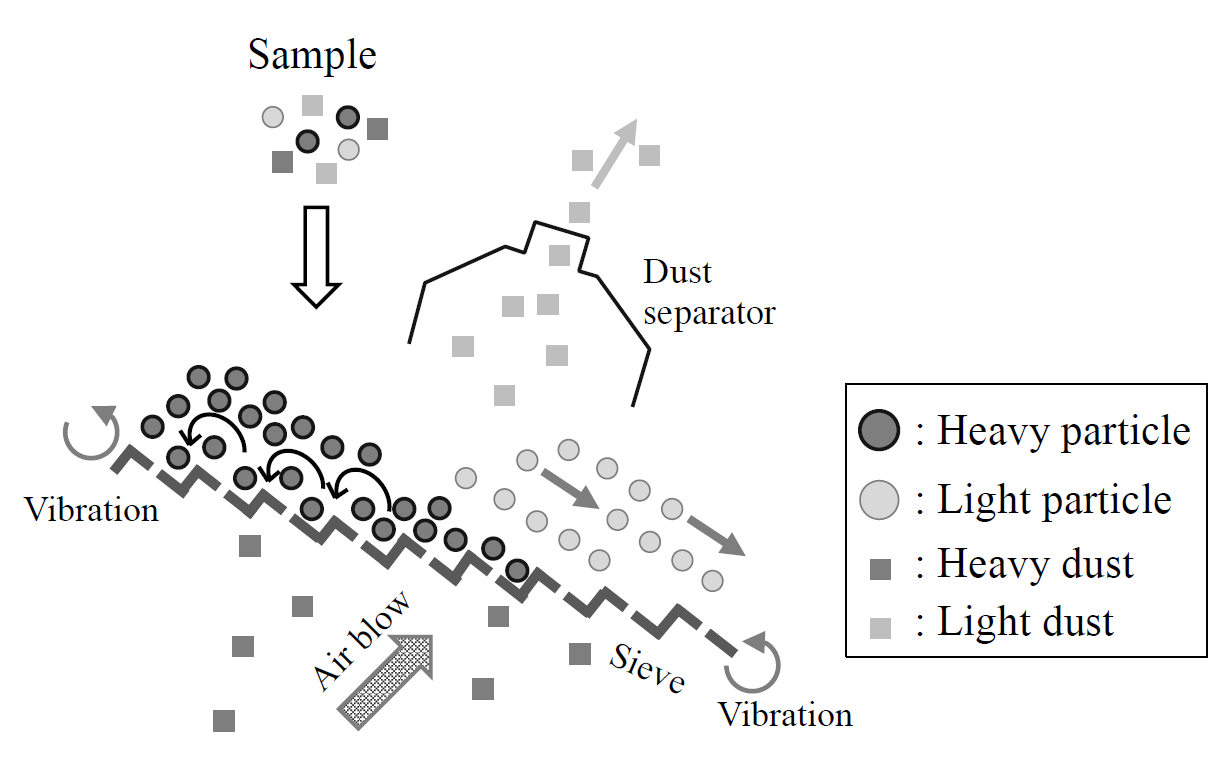
The reaction of natural pozzolans is caused by volcanic glass composed of amorphous silicate; however, volcanic ejecta also contains crystal mineral, pumice, and sometimes weathered clay fraction in their natural conditions. By focusing on the differences of physical properties between these components, high-purity volcanic glass powder (VGP) was manufactured by dry gravity classification and pulverization. This paper reports the results of investigations to utilize pyroclastic flow deposits as a supplementary cementitious material (SCM).
Through this method, the glass content of VGP increased to 88% with a mean particle size of 1 μm, when that of the raw material is about 60%. Chemical analysis indicated that VGP is principally composed of silica (about 72%) and alumina (about 13%).
The performance of VGP as a SCM was evaluated by conducting tests on concrete mixtures, replacing 0% to 30% by weight of portland cement by VGP with a 20% to 60% water to cement ratio. VGP concrete showed better results of 7-and 28-day compressive strength compared to control concrete in all experiments. In particular, VGP demonstrated better flowability and strength development in concrete with a low water-binder ratio in comparison to silica fume.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain copyright of the articles published in RILEM Technical Letters and grant the journal the right of first publication with open access. The work is simultaneously licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) that allows others to share and adapt the work under the following terms: 1) a proper attribution is given in a form of a reference to the original work's authorship and initial publication in RILEM Technical Letters (bibliographic record with the DOI link); 2) a link to the license is provided; 3) the changes (if any) are indicated.









