Estimating Na+ and K+ concentrations of the pore solution based on ex-situ leaching tests and thermodynamic modeling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21809/rilemtechlett.2022.164Keywords:
Cement, Pore solution, Leaching, Thermodynamic ModelingAbstract
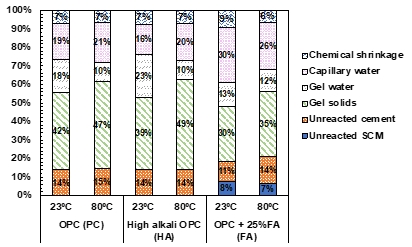
Ex-situ leaching (ESL) methods have typically yielded higher sodium and potassium concentrations than pore solutions obtained using the conventional high-pressure extraction approach since ESL concentrations require a back-calculation to account for dilution. This paper proposes a new method for adjusting the concentrations obtained from ESL. Thermodynamic calculations were used to determine the total pore solution content, and a pore partitioning model was then used to separate the total solution into gel and capillary assignments. Using the refined pore solution volumes to adjust the concentrations from ESL improved the correlation to PSE concentrations.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Atolo Tuinukuafe, Krishna Siva Teja Chopperla, Jason Weiss, Jason Ideker, Burkan Isgor

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright of the articles published in RILEM Technical Letters and grant the journal the right of first publication with open access. The work is simultaneously licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) that allows others to share and adapt the work under the following terms: 1) a proper attribution is given in a form of a reference to the original work's authorship and initial publication in RILEM Technical Letters (bibliographic record with the DOI link); 2) a link to the license is provided; 3) the changes (if any) are indicated.









