Cathodic protection in reinforced concrete structures affected by macrocell corrosion: a discussion about the significance of the protection criteria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21809/rilemtechlett.2017.38Keywords:
Impressed Current Cathodic Protection, corrosion of steel in concrete, potential mapping, electrochemical modellingAbstract
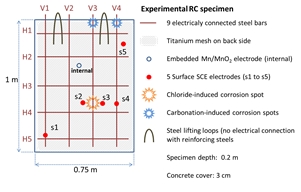
Cathodic protection is a technique that has been used to control corrosion and increase the service life of reinforced concrete structure. Standards as EN ISO 12696 give protection criteria for both impressed current and sacrificial anodes techniques, based on potential value or decay during a depolarization sequence. The polarization (current ON) and depolarization (current OFF) is experimentally studied on a corroded concrete wall thanks to six references electrodes and compared to a time-dependent modelling using FEM software COMSOL Multiphysics. Both experimental and numerical results show significant differences in the time response according to electrode location. This conclusion indicates that the concept of protection criteria defined by the standards is not suitable to assess the efficiency of cathodic protection applied to reinforced concrete structure.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain copyright of the articles published in RILEM Technical Letters and grant the journal the right of first publication with open access. The work is simultaneously licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) that allows others to share and adapt the work under the following terms: 1) a proper attribution is given in a form of bibliographic record with the DOI link directing to RILEM Technical Letters; 2) a link to the license is provided; 3) the changes (if any) are indicated.









